Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the same tree where every subtree (of the given tree) not containing a 1 has been removed.
A subtree of a node node is node plus every node that is a descendant of node.
Example 1:
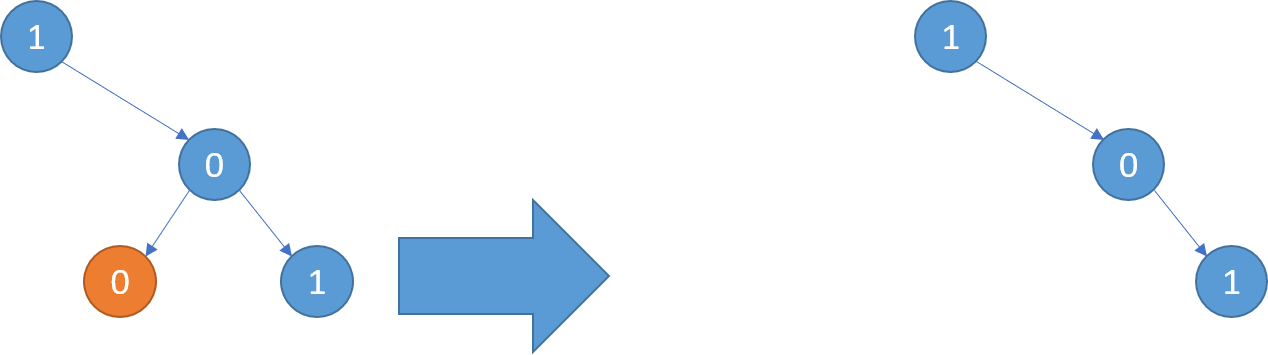
1 | Input: root = [1,null,0,0,1] |
Example 2:
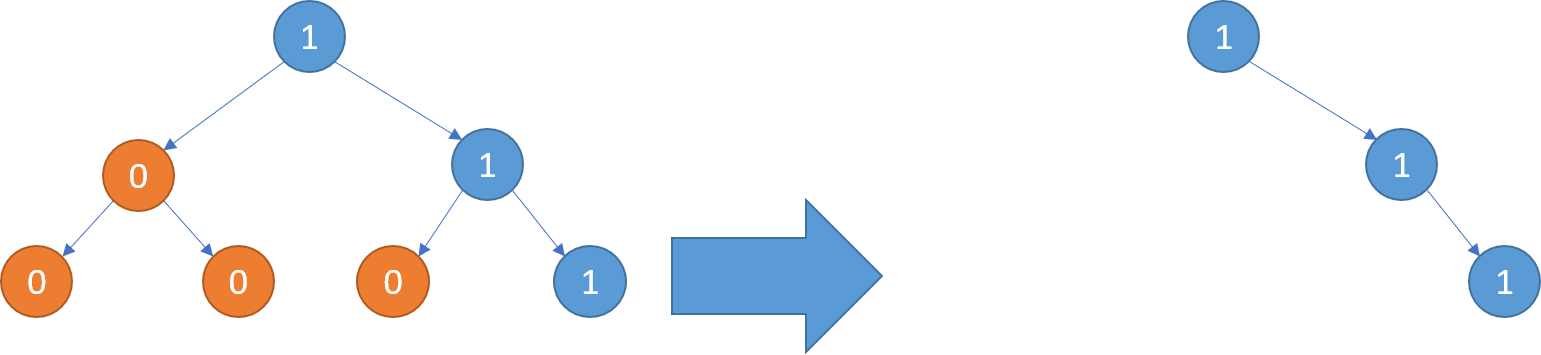
1 | Input: root = [1,0,1,0,0,0,1] |
Example 3:
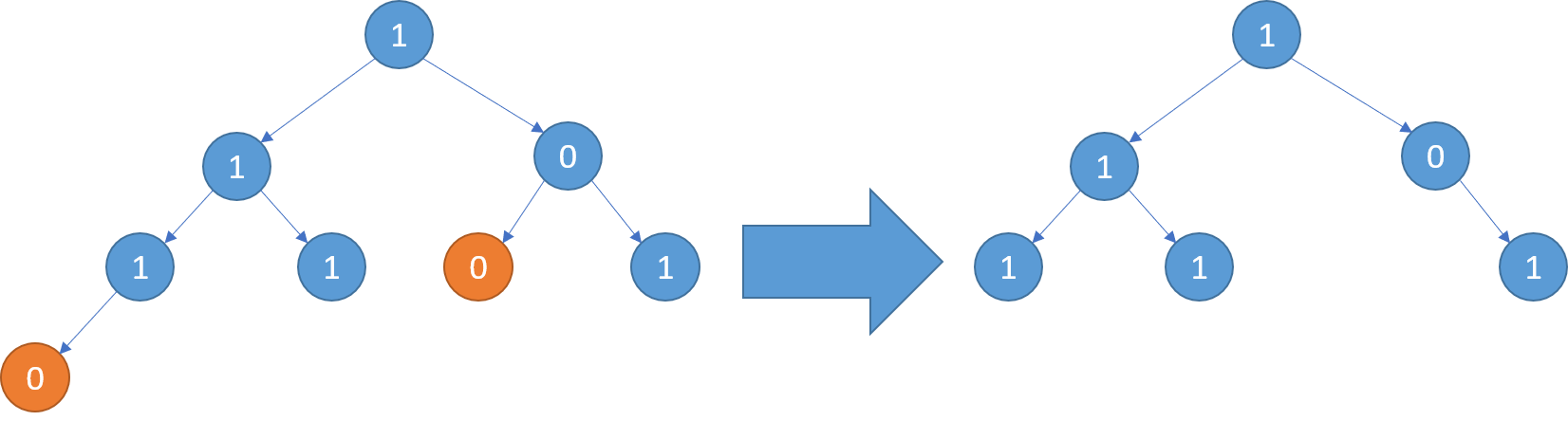
1 | Input: root = [1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0] |
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 200].
Node.val is either 0 or 1.
Solutions
This is a post-order traversal
If the following conditions are met, delete the current leaf node
- Left subtree is None
- The right subtree is None
- The current root value is 0
1 | # O(n) time | O(n) space |